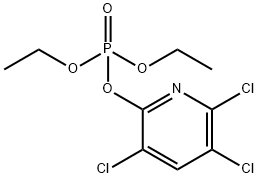
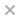体内研究
Chlorpyrifos-oxon (CPO) is rapidly detoxified by human liver microsomes via CYP-dependent deethylation and dearylation, and by glutathione-S-transferase. In addition, reactions with A-esterases such as paraoxonase 1 (PON 1) or B-esterases such as carboxylesterase and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) in the liver may rapidly degrade or scavenge Chlorpyrifos-oxon.
Chlorpyrifos-oxon (3 mg/kg, ip; once; wild-type mice) treatment shows the dimensions of microtubules from Chlorpyrifos-oxon-treated mice are about 60% of those from control mice. The microtubules from mice exposed to Chlorpyrifos-oxon have covalently modified amino acids and abnormal structure, suggesting disruption of microtubule function.