体外研究
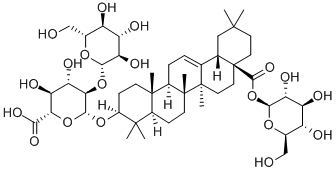
Ginsenoside Ro in
Panax ginseng
is a beneficial novel Ca
2+
-antagonistic compound and may prevent platelet aggregation-mediated thrombotic disease. Ginsenoside Ro dose-dependently reduces thrombin-stimulated platelet aggregation, and IC
50
is approximately 155 μM. Ginsenoside Ro inhibits TXA
2
production to abolish thrombin-induced platelet aggregation. Thromboxane A
2
(TXA
2
) induces platelet aggregation and promotes thrombus formation. Ginsenoside Ro dose-dependently (50-300 μM) reduces the TXB
2
level that is induced by thrombin; Ginsenoside Ro (300 μM) inhibits the thrombin-mediated elevation in TXB
2
level by 94.9%. COX-1 activity in the absence of Ginsenoside Ro (negative control) is 2.3±0.1 nmol/mg protein. However, Ginsenoside Ro dose-dependently (50-300 μM) reduces its activity; at 300 μM, COX-1 activity is reduced by 26.4% of that of the negative control. TXA
2
synthase (TXAS) activity in the absence of Ginsenoside Ro (negative control) is 220.8±1.8 ng/mg protein/min. However, Ginsenoside Ro dose-dependently (50-300 μM) reduces its activity; at 300 μM, TXAS activity is reduced by 22.9% of that of the negative control. The inhibitory effect of Ginsenoside Ro (300 μM) on TXB
2
production (94.9%) is significantly higher than those on COX-1 (26.4%) and TXAS (22.9%) activities. To assess the toxicity of Ginsenoside Ro in Raw 264.7 cells, they are first treated with various concentrations (10 μM, 50 μM, 100 μM, and 200 μM) of Ginsenoside Ro for 24 h. Ginsenoside Ro exhibits no significant dose dependent toxicity. The effect of Ginsenoside Ro is next determined on cell viability and ROS levels, a marker of oxidative stress, following treatment with 1 μg/mL LPS. LPS reduces cell viability by ∼70% compared with nontreated controls. Pretreatment with 100 μM and 200 μM Ginsenoside Ro for 1 h prior to 1 μg/mL LPS incubation for 24 h leads to a significant increase in cell viability. The changes in ROS levels and NO production are consistent with the effects of Ginsenoside Ro on viability.